Adblocker Detected

We always struggled to serve you with the best online calculations, thus, there's a humble request to either disable the AD blocker or go with premium plans to use the AD-Free version for calculators.
Disable your Adblocker and refresh your web page 😊
Table of Content
Try this normal force calculator to determine the amount of force a surface applies on an object to prevent it from falling.
The normal force is exerted on an object by a surface. For instance, you have a glass and you put it on a table, and the gravitational force pulls the glass downward. To stop the glass from going down the table exerts a force on it.
This force that is exerted by the table is known as the normal force.
It is denoted by \(F_N\) or N and the unit that is used for the normal force is Newton. This normal force follows the principle of Newton’s Third Law of Motion.
Normal force acts perpendicular to the surface and it changes on whether the object is on an incline or a flat surface.
The formula that is used for knowing the normal force on a thing that is placed on a horizontal surface is as follows:
\(Normal\ Force\ =\ F_N = m.g\)
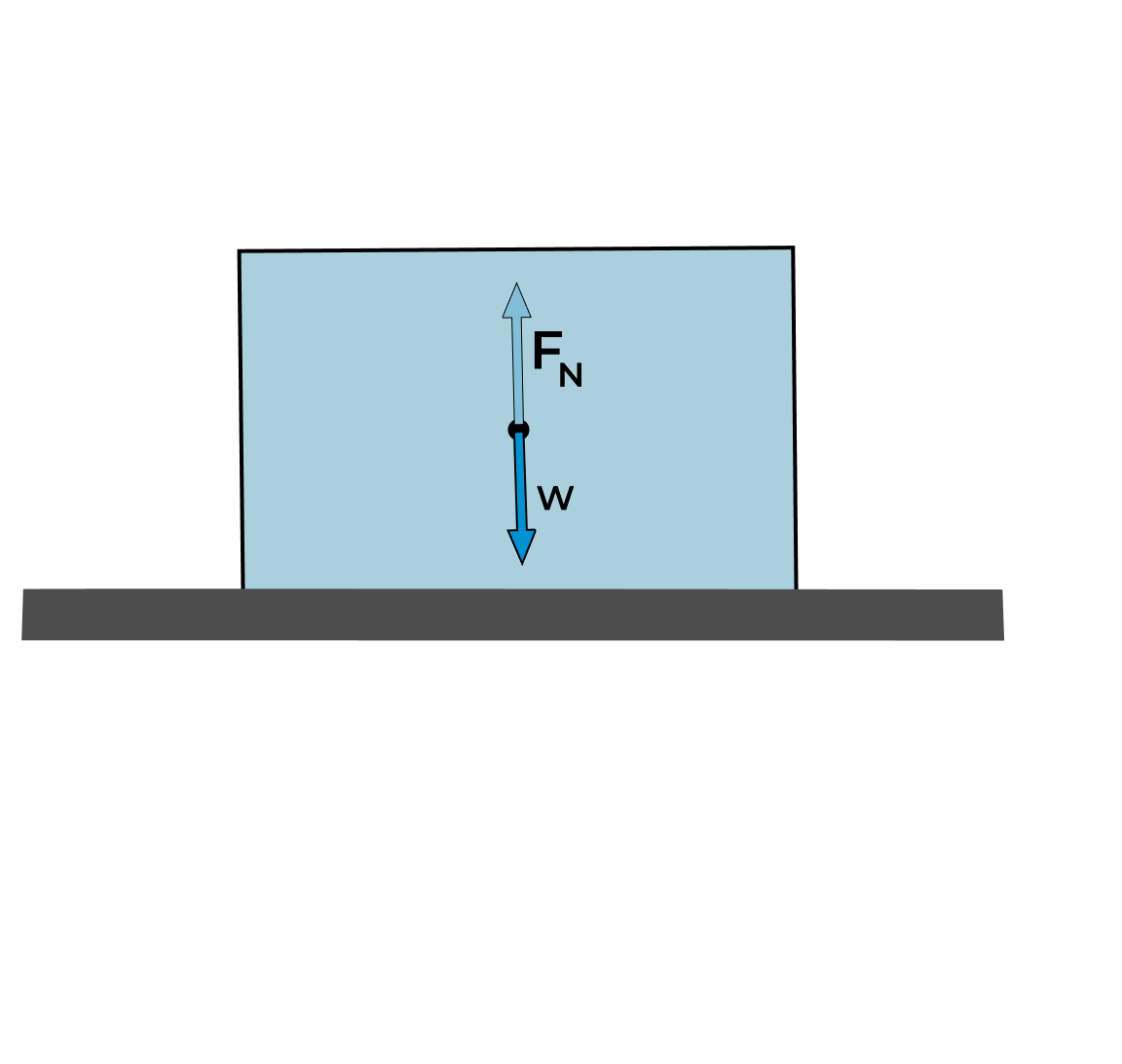
Where
If the object is placed on an inclined surface then the normal force on an incline is:
\(Normal\ Force\ =\ F_N = m.g.cos(a)\)

Where
When the object is placed on a horizontal surface and an external force acts on it in an upward direction then the normal force equation is as follows:
\(Normal\ Force\ =\ F_N = m.g – F.sin(x)\)
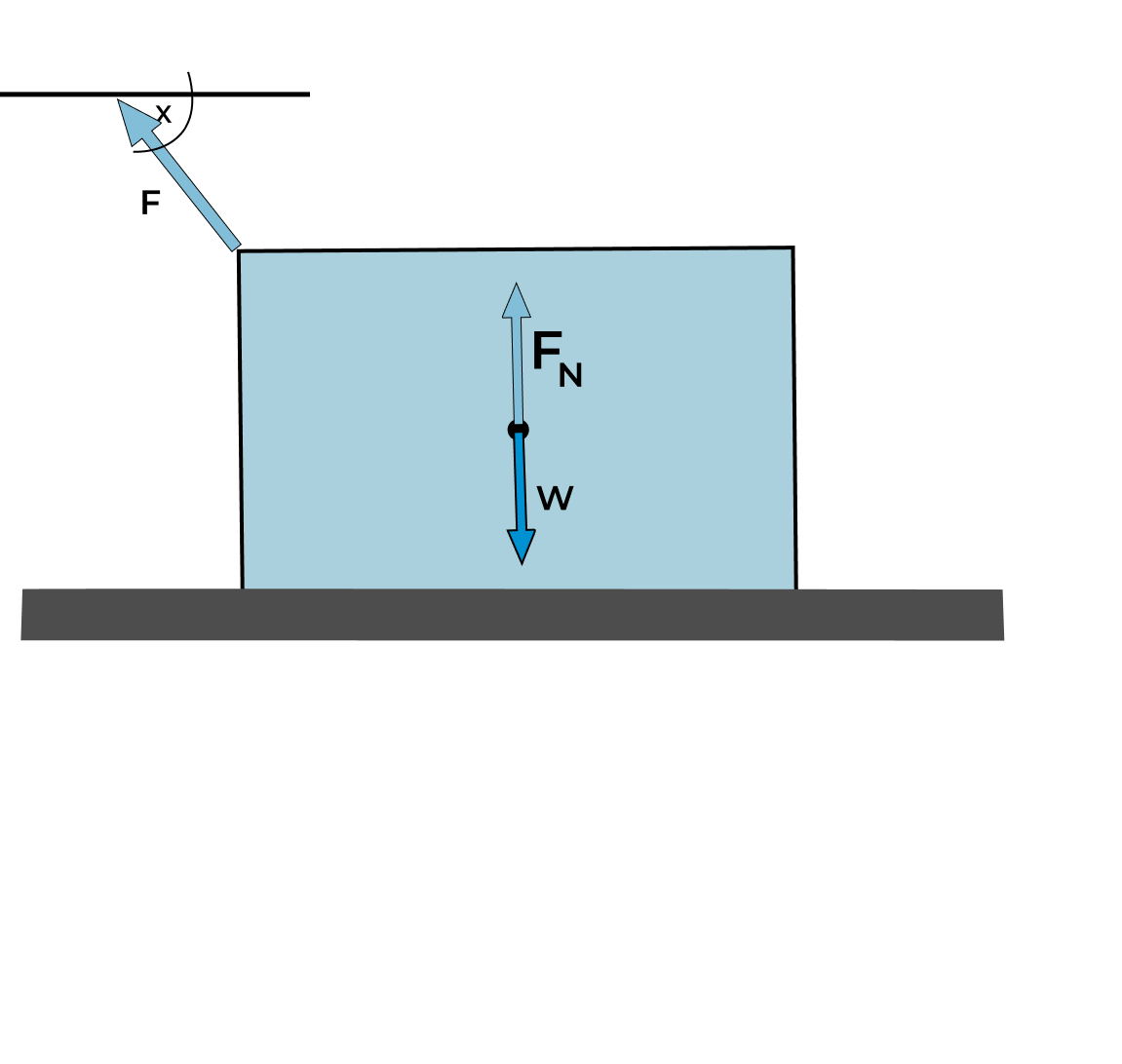
Where
If the object is present on a horizontal surface and an external force acts on it in the downward direction then the formula of normal force is:
\(Normal\ Force\ =\ F_N = m.g + F.sin(x)\)

Solution:
Mass = m = 1 Kg
Angle = θ = 45°
\(F_N = m * g * cos(α)\)
Substituting the values in the normal force formula
\(\text{Normal Force} = F_{N}\)
= 1 * 9.8 * cos (45°)
= 6.92N
Solution:
Given that:
F = 200 N
m = 20 kg
g = 9.8 ms^-2
θ = 30°
Using the formula we get,
\(Normal\ Force\ =\ F_N = mg + Fsin θ\)
\(Normal\ Force\ =\ F_N = 20 (9.8) + 200* sin (30°)\)
\(F_N = 196 + 200 (1/2)\)
\(F_N = 196 + 100\)
\(F_N = 296 N\)