Adblocker Detected

We always struggled to serve you with the best online calculations, thus, there's a humble request to either disable the AD blocker or go with premium plans to use the AD-Free version for calculators.
Disable your Adblocker and refresh your web page 😊
The free online arctan calculator allows you to find the inverse tangent function or arctan (x) in radians, degrees, and different units. Just enter the tangent value and lets the tool do the remaining trigonometric calculations. The inverse tangent calculator supports the input of decimal numbers like 0.5, 0.86, -0.9, etc.
Well, this context specifically created to provides you with how to calculate arctan (tan inverse) of the given tangent value, even some terms that you should have an idea about!
In trigonometric functions, the arctangent represents the inverse tangent function of x. In this phenomenon, \( x \) is real \( (x ∈ ℝ)\). To calculate arctan When the tangent of \( y \) is equal to \( x \), it indicates that \( tan y = x\). In this condition the arctangent of x will be equal to the inverse tangent function of \( x\), therefore \( y arctan x= tan-1 x = y\). However, the most convenient way to handle this inverse trigonometric function is to use a tan inverse calculator.
To find the inverse of tangent you can use its following formula:
$$ y = tan(x) | x = arctan(y) $$
Also, you could use the arctan calculator for calculating inverse tangent, instead of using the above formula.
Example
If the tangent of \( 45^o \) is equal to 1
So
$$ arctan 1 = tan^{-1} (1) = 45° $$
$$ 45°= 45 * π/180 = 1.548 rad $$
Using an inverse tangent calculator is the best way to complete the calculation that involves taking the inverse of tangent. Furthermore, it helps to find an arctan in degrees, radians and relevant units. If the arctan of 1 is 50 then to find the inverse tangent have a look on following calculations:
$$Arctan 50 = tan^{-1} 50 = 88^° 51^’ 15.254″$$
$$= 88.85424 + k * 180° (k = -1,0,1,…)$$
$$= -91.14576°, 88.85424°, 268.85424°, …$$
$$= 1.5508 rad + k * π (k = -1,0,1,…)$$
$$= -0.50637π, 0.49363π, 1.49363π, …$$
However, you can use unit circle point calculator that helps you to find the circle trigonometry functions corresponding to the unit circle.
Specifically, an angel can be calculated by trying a simple formula manually. Although, if you’re looking for the fastest way to find arctan, then an arctan calculator is the best option. So to find an angle:
$$ arctan(θ) or tan-1(θ)$$
$$ tan(θ) = a/b$$
$$ (θ) = arctan*a/b$$
The following table showing you some common tangent values and the arctan, or angles. However, to use arctan calculator you do not have to memorize these values. In manual calculation, they might be a great help.
|
Y |
X = arctan(y) |
|
|
Angle (degrees) |
Angle (Radians) |
|
| -∞ | -90° | –π/2 |
| -√3 | -60° | –π/3 |
| -1 | -45° | –π/4 |
| –√3/3 | -30° | –π/6 |
| 0 | 0° | 0 |
| √3/3 | 30° | π/6 |
| 1 | 45° | π4 |
| √3 | 60° | π/3 |
| ∞ | 90° | π/2 |
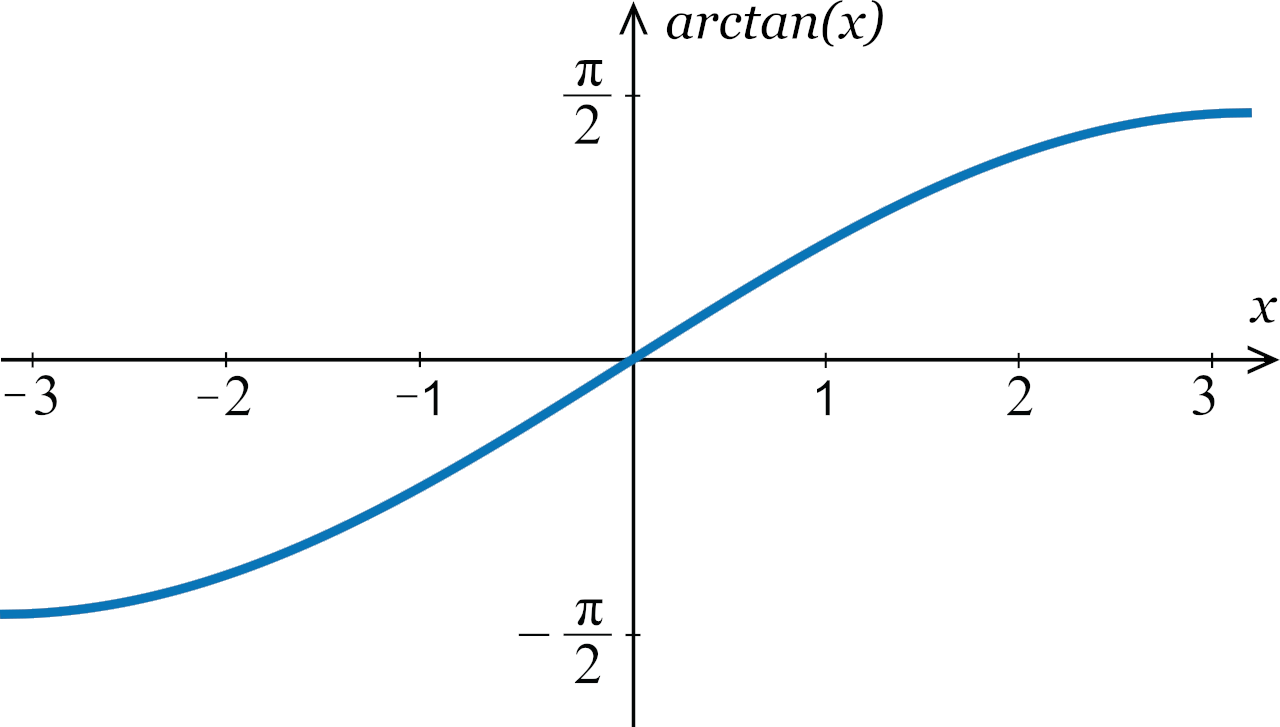
If you want to graph the arctan function for any expected value of tangent, then it forms a curve that will starts from \( (-∞, \frac{–π} {2}) \) and terminates at \( (∞, \frac {π}{2})\).
Inverse tan Calculator makes the calculation quicker and error-free. To understand it, you just need to follow the step explained below:
Input
Output
The inverse tan calculator calculates:
Furthermore, An online arccos calculator helps you to demonstrate the inverse of the cosine of a certain number.
Adding 180 degrees to arc tangent because it is not possible to have a function of one to many. Therefore, Limiting the theta from \( \frac{-π}{2} to \frac{π}{2}\) guarantees that the inverse tangent a one-to-one function. In this way, you can get inverse tangent on quadrant 1 and 4.
As The range of inverse tangent is from \( \frac{-π}{2} to \frac{π}{2}\) so tan inverse(infinity) will be equal to= \( \frac {π}{2} Tan90°.
No, it does not converge. In the case of arctan1x, as x gets bigger, the series will turn into the harmonic series, which only diverges instead of converging.
The value of inverse tangent minus infinity is equal to is \( -90 \) degrees. It will lie in the fourth quadrant. To measure it you have to go origin clockwise from the x-axis.
Arctan calculator serves as an easy way to deal with one of the most complex trigonometric function related to tangent value. On the other hand, tan inverse might get confusing by applying a formula or using a table. Therefore, this calculator provides a great learning opportunity for teachers and students to master this inverse function. You just have to follow the commands to have your final output. It helps all those learners as well who are unaware of trigonometry as it offers a very user-friendly interface!
From the source of Wikipedia: Principle Values, Equal identical trigonometric functions, Arctangent addition.
From the source of wolfram: Scope, Applications, Properties and relations, Possible Issues.
From the source of ExcelJet: Convert result to degree, Difference between Arctan and Arctan2.