Adblocker Detected

We always struggled to serve you with the best online calculations, thus, there's a humble request to either disable the AD blocker or go with premium plans to use the AD-Free version for calculators.
Disable your Adblocker and refresh your web page 😊

Disclaimer:The results generated by the tool should be considered for educational purposes only. You are notified to consult an expert in case you consider calculations as a reference anywhere.
Table of Content
Our best dilation calculator is specifically designed to calculate the coordinates of the center point of the modified image after it gets transformed from its original size.
But before you become familiar with our dilation scale factor calculator, you need to have a more in-depth understanding of some terms.
In geometry,
“A significant transformation in the size of an image without changing its shape is known as dilation.”
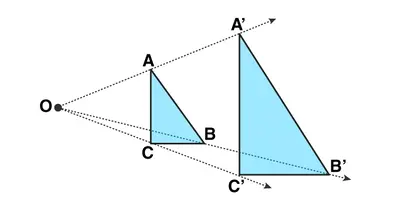
What do you actually see in this picture? Do not panic! Let us tell you what is it!
In the above picture:
You can trace this change in distance of the coordinates by using our free online dilation calculator.
Generally, we have two types of dilation which are as follows:
Enlargement:
When an image gets larger in size just after the dilation is performed, then it is known as enlargement.
Reduction:
If there is any contraction in the size of the image after you perform dilation, then it is said to be a reduction.
Horizontal dilation:
This type of dilation occurs for a function y = f(x) which dilates the function by a scale factor C using the following equation:
$$ Y = f\left(Cx\right) $$
Vertical dilation:
The function y = f(x) dilates vertically wwit a scale factor C using the expression below:
$$ Y = C * f\left(x\right) $$
“The ratio of the size of the modified image to the original one is known as the scale factor”
Scale factor actually defines the change in the size of the image. Keep in mind that:
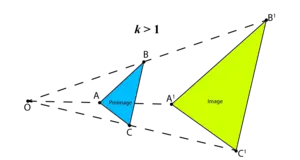
If SF >1, the image contracts or gets smaller.
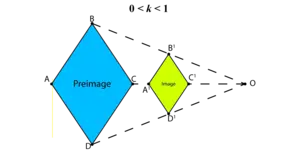
If 0 < SF < 1, the modified image gets shrinked.
If SF = 1, the modified image remains un-altered in both shape and size.
Here if you want to determine only scale factor, you can also make use of our best scale factor calculator for free.
After the dilation is done, the only change that occurs is the change in the distance between the coordinates. Also, you will notice that some factors are not changed during the transformation of the images from their original size to the modified one. These include:
You must be thinking that it is going to be something tricky. But believe us it is not. Let us solve some examples so that you understand the dilation properly. Stay focused!
Example # 01:
Just suppose we have a triangle ABC in the coordinate system. The coordinates of vertices of the triangle are as follows:
$$ A(2, 8), (1, -2), (3, 5) $$
Now, if the scale factor is 5, what is the center of dilation OA’, OB’, OC’.
Solution:
As the given coordinates are:
$$ A(2, 8), (1, -2), (3, 5) $$
Here we suppose our origin O(0, 0) as the center of the original triangle.
Determining the center of dilation as follows:
$$ OA’ = \left(2 * 5, 8 * 5\right) $$
$$ OA’ = \left(10, 40\right) $$
Now we have:
$$ OB’ = \left(1 * 5, -2 * 5\right) $$
$$ OB’ = \left(5, -10\right) $$
Similarly;
$$ OC’ = \left(3 * 5, 5 * 5\right) $$
$$ OC’ = \left(15, 25\right) $$
Here you can also use our free dilations calculator to get immediate results. Believe us the whole process is free of cost!
Example # 02:
A square has a center at origin and its corners has coordinates as follows:
$$ A(1, 2), (2, -2), (3, 4), (6, 2) $$
If the scale factor is ½, how to find scale factor of dilations?
Solution:
As the center of the square is at origin, so we have:
O(0, 0)
As we know that:
The points with respect to the origin of the dilated image are OA’, OB’, OC’, OD’.
Determining the coordinates of the dilated image.
$$ OA’ = \left(1 * \frac{1}{2}, 2 * \frac{1}{2}\right) $$
$$ OA’ = \left(\frac{1}{2}, 1\right) $$
$$ OA’ = \left(0.5, 1\right) $$
Now:
$$ OB’ = \left(2 * \frac{1}{2}, -2 * \frac{1}{2}\right) $$
$$ OB’ = \left(1, -1\right) $$
$$ OC’ = \left(3 * \frac{1}{2}, 4 * \frac{1}{2}\right) $$
$$ OC’ = \left(\frac{3}{2}, 2\right) $$
$$ OC’ = \left(1.5, 2\right) $$
At last, we have:
$$ OD’ = \left(6 * \frac{1}{2}, 2 * \frac{1}{2}\right) $$
$$ OD’ = \left(3, 1\right) $$
Our free dilation graph calculator is very authentic and widely used by scholars to design various 2D and 3D images. If you are one of them and want to take advantage, jump down a little!
Input:
Output:
Our free triangle dilation calculator finds:
When a gravitational field causes a change in the time lapse, then it is said to be as gravitational time dilation.
If you multiply the scale factor ½ with the coordinates of the point of the original image, the modified image will shrink for sure. But if you multiply the coordinates of the real image with the scale factor of 6, the final image gets enlarged.
In applications like thermal expansion and contraction, dilation has a great importance as it is the change in the original position.
Dilation has its branches spread in the galaxy of graphic designing and architecture. Also doctors make a proper use of it for examining a patient’s eye better. To provide firm support to professionals and pupils around the globe, we have developed a free online dilation calculator so that they could get the awesome benefit of this opportunity.
From the source of wikipedia: Scale factor, Dilation
From the source of khan academy: Identify scale factor, Scale copies
From the source of lumen learning: Simultaneity And Time Dilation, Time Dilation, The Twin Paradox.