Adblocker Detected

We always struggled to serve you with the best online calculations, thus, there's a humble request to either disable the AD blocker or go with premium plans to use the AD-Free version for calculators.
Disable your Adblocker and refresh your web page 😊
Table of Content
The mole ratio calculator calculates the ratio of moles between reactants and products based on the balanced chemical equation of the reaction.
“Mole ratio is a conversion factor that proportionally relates the amounts of chemical substances involved in a reaction
SI Unit: Mole
Mole Ratio = Moles of Reactants/Moles of Products
The values here come from the coefficient of the chemical reaction.
Consider the following balanced chemical equation:
\({N_2} \left( g \right) + 3{H_2} \left( g \right) \rightarrow 2{NH_3} \left( g \right)\nonumber\)
The reaction has 6 mole ratios, elaborated as:
\(\begin{array}{ccc}\dfrac{3 \: \text{mol} \: {H_2}}{1 \: \text{mol} \: {N_2}} & or & \dfrac{1 \: \text{mol} \: {N_2}}{3 \: \text{mol} \: {H_2}} \\ \dfrac{1 \: \text{mol} \: {N_2}}{2 \: \text{mol} \: {NH_3}} & or & \dfrac{2 \: \text{mol} \: {NH_3}}{1 \: \text{mol} \: {N_2}} \\ \dfrac{3 \: \text{mol} \: {H_2}}{2 \: \text{mol} \: {NH_3}} & or & \dfrac{2 \: \text{mol} \: {NH_3}}{3 \: \text{mol} \: {H_2}} \end{array}\nonumber\)
Related: If you have any reaction that is unbalanced, you can use the balancing chemical equations calculator to balance it.
Calculating mole ratios helps to estimate the theoretical yield of a chemical reaction. To calculate it, follow the steps below:
Consider you have the following reaction:
\({N_2} \left( g \right) + 3{H_2} \left( g \right) \rightarrow 2{NH_3} \left( g \right)\nonumber\)
If 5.83 moles of hydrogen reacts with the excess amount of nitrogen, how many moles of ammonia will be produced after the reaction completes?
Step # 01: Write the Given Values
Moles of \(H_2\) = 5.83
Step # 02: Now Write Down the Unknown Quantity
Moles of \(NH_3\) = ?
Step # 03: Identify the Nature of the Problem
The given reaction is converting \(H_2\) into \(NH_3\) moles. So we will ignore the \(N_2\) completely. Our main concern is to find a conversion factor that allows us to write \(NH_3\) in the numerator and \(H_2\) in the denominator.
Step # 04: Solve
\(5.83 \: \text{mol} \:{H_2} \times \dfrac{2 \: \text{mol} \:{NH_3}}{3 \: \text{mol} \:{H_2}} = 3.88 \: \text{mol} \:{NH_3}\nonumber\)
Using our calculator lets you understand the stoichiometric relationships between the chemical species in a reaction. Learn how to use the tool to obtain accurate and instant results for molar ratios.
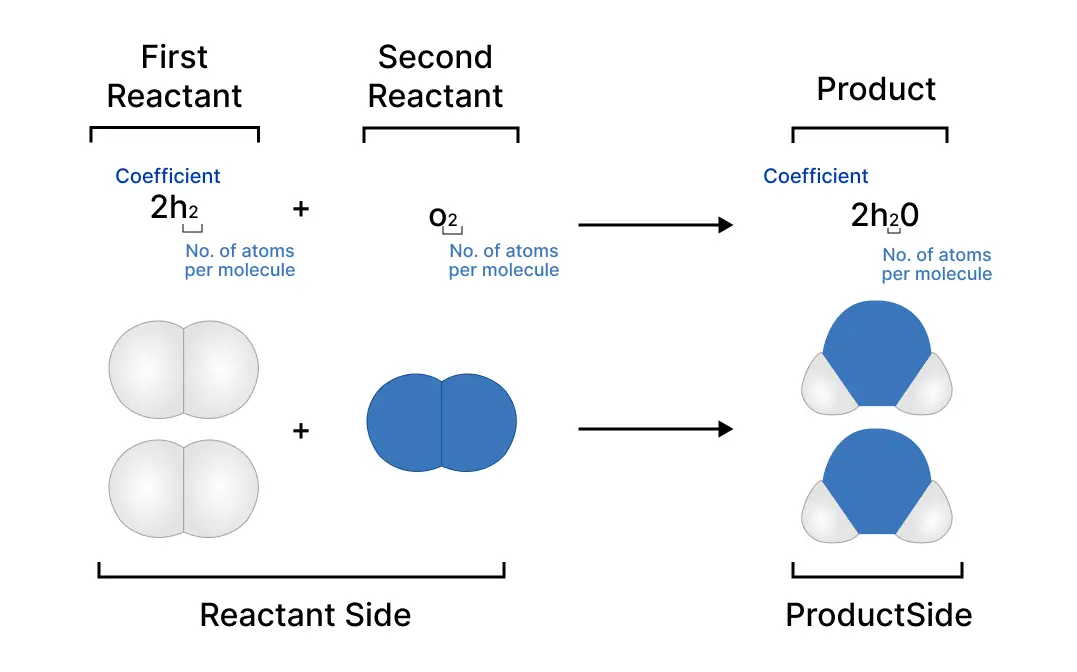
As seen from the following balanced equation:
\(2H_2 + O_2 ⟶ 2H_2O\)
Mole Ratio = 2:1